Configuring Cloud Foundry to route traffic to apps on custom ports
Page last updated:
By default, apps only receive requests on port 8080 for both HTTP and TCP routing. Configuring custom app ports allows developers to bring workloads onto
Cloud Foundry that receive requests on ports other than 8080. Here are some example use cases:
Serving web client requests on one port, and stats and debugging on another
Using TCP protocols that require multiple ports
Running Docker images on Cloud Foundry
To use the apps and route_mappings Cloud Controller API endpoints to update the ports so the the app can receive requests, see Procedure.
Flow of a request to an app
The table describes the Network Address Translation that occurs in the data path of a client request:
| Port Type | Description | Network Hop |
|---|---|---|
| Route port | The port to which a client sends a request | Client to load balancer, load balancer to Gorouter |
| Back end port | The port on the VM where an application container is hosted, which is unique to the container | Gorouter to Diego Cell |
| App port | The port on the container, which must match a port on which the app is configured to receive requests | Diego Cell to application container |
The following diagram shows an example data path and Network Address Translation for TCP routing:
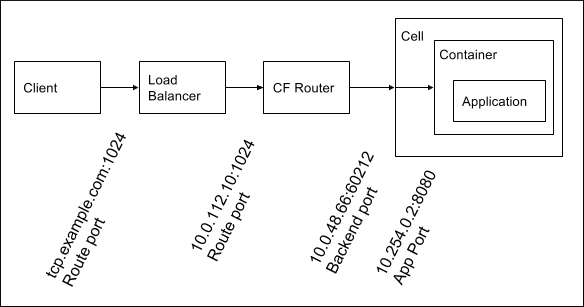
For HTTP routing, the route port is always 80 or 443.
Prerequisites
Before you follow the procedure to configure routing to your app on custom ports, you must have:
An app pushed to Cloud Foundry that can receive requests on one or more custom ports.
Routes for which you want traffic forwarded to your app on custom ports, which are mapped to the app.
If your app receives requests on two ports, and you want clients to be able to send requests to both of them, create two routes. These routes can be from HTTP or TCP domains.
Procedure
In the following procedure, use API endpoints to map the routes to your app on the ports it uses to receive requests. For more information about routes, see Routes and Domains.
To configure your app to receive HTTP or TCP requests on custom ports:
Run:
cf app APP-NAME --guidWhere
APP-NAMEis the name of your app.From the output, record:
- Under
guid, the global unique identifier (GUID) of your app. - Under
type, the process type your app uses.
- Under
Retrieve the GUIDs of the routes for your app by running one of these commands, depending on whether your app uses HTTP or TCP routes:
For HTTP routes, run:
cf curl /v3/apps/APP-GUID/routes?hosts=ROUTE-HOSTNAMEWhere:
APP-GUIDis the GUID of your app that you recorded in an earlier step.ROUTE-HOSTNAMEis the subdomain of the domain associated with the route. For example, in the routeexample-app.shared-domain.example.com, the host name isexample-app.
For TCP routes, run:
cf curl /v3/apps/APP-GUID/routes?port=PORTWhere:
APP-GUIDis the GUID of your app that you recorded in an earlier step.PORTis the port to which the TCP route sends requests.
From the output, record the GUIDs of the routes for your app.
For each route, update the ports to which it sends requests by running:
cf curl -X PATCH /v3/routes/ROUTE-GUID/destinations -d '{ "destinations": [ { "app": { "guid": "APP-GUID", "process": { "type": "PROCESS-TYPE" } }, "port": PORT, "protocol": "PROTOCOL" } ] }'Where:
APP-GUIDis the GUID of your app that you recorded in an earlier step.ROUTE-GUIDis the GUID of a route that you recorded in an earlier step.PORTis a custom port on which your app is configured to receive requests.PROTOCOLis the protocol that the route uses. For HTTP routes, this value is eitherhttp1orhttp2. For TCP routes, this value istcp.PROCESS-TYPEis the value oftypethat you recorded in an earlier step. This value is usuallyweb.
This API call removes all destinations for a route and replaces them with the destinations you provide in the API request.
Additional resources
- For more information about making requests to the Cloud Controller API (CAPI)
appsendpoints, see the CAPI V3 documentation.